Artificial intelligence (AI) is reshaping the global labor market, and Mexico is no exception. This is revealed by the latest AI Barometer in the Labor Market 2025, prepared by PwC, which provides a detailed analysis of the impact of this technology on employment, required skills, and formal education in the country.
The study offers revealing data on the most affected sectors, the emerging opportunities, and the challenges that companies, workers, and business leaders face in adopting artificial intelligence.
ALSO READ. Google’s AI Mode: Is this the end of the internet as we know it?
What is PwC’s AI Barometer in the Labor Market?
The AI Barometer in the Labor Market 2025, developed by PwC, is a global analysis that examines nearly one billion job postings and thousands of corporate reports across six continents. In Mexico’s case, more than 18 million observations were evaluated to understand how artificial intelligence is reshaping the labor landscape.
This report measures the current impact and identifies trends, projections, and opportunities that will shape the future of employment in Mexico. Its value lies in providing companies, leaders, and decision-makers with a roadmap to navigate the changes driven by artificial intelligence.
ALSO READ. How is Google’s AI mode different? This is how it works
How has the demand for AI-related jobs evolved in Mexico?
Between 2021 and 2024, Mexico experienced sustained growth in job postings requiring artificial intelligence skills. According to PwC, the demand recorded a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 33.6%, reflecting the increasing interest in AI-trained professionals.
However, 2024 brought an economic slowdown that affected the overall labor market, causing a decline in the percentage of AI-related vacancies. While 55,000 job offers were posted in 2023, by 2024 the number dropped to 42,000, representing just 0.8% of total vacancies.
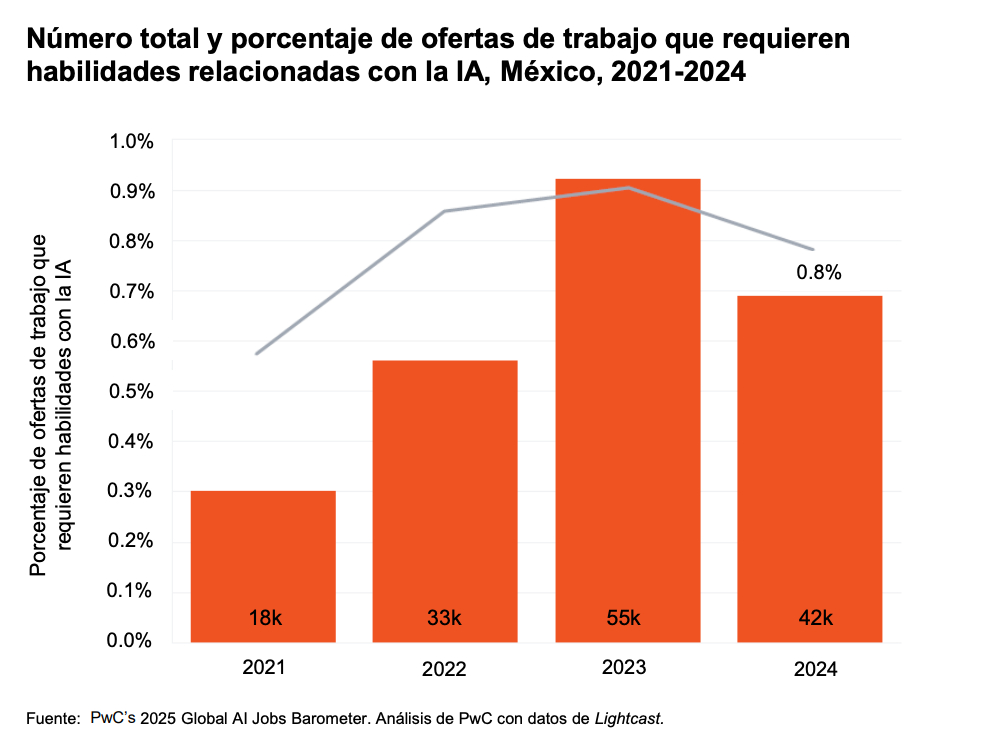
This data suggests that although artificial intelligence remains a strategic area, its integration faces ups and downs due to the national economic context.
Which sectors are looking for AI-skilled talent?
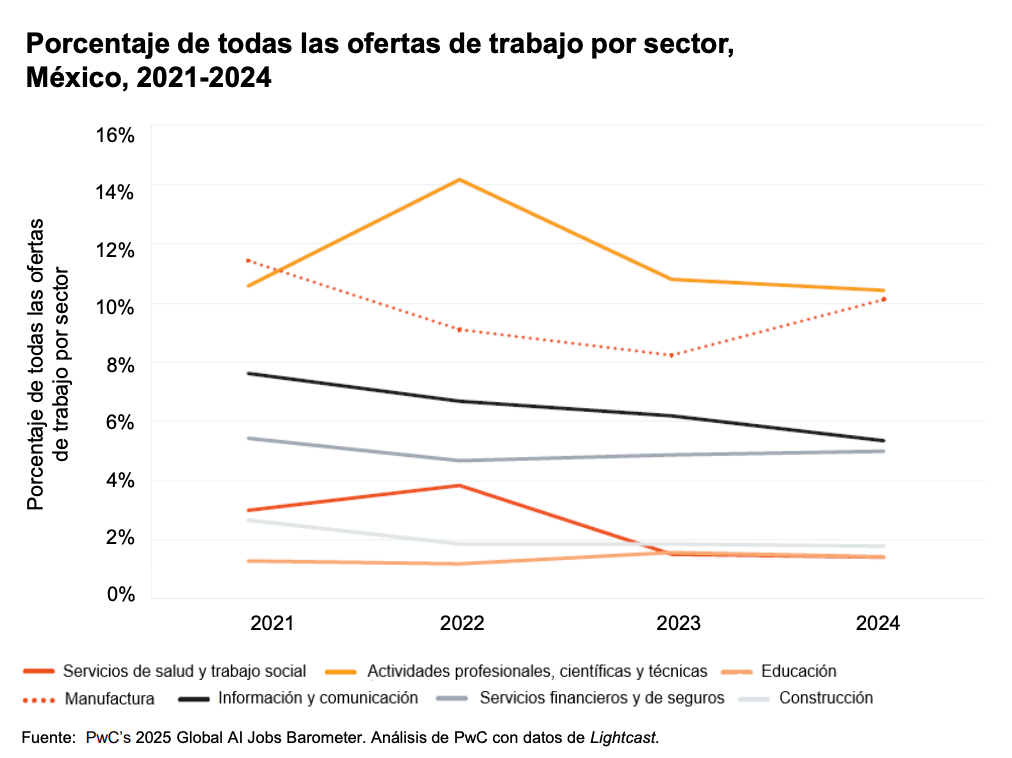
The PwC report identifies that the professional, scientific, and technical services sector remains the largest employer in Mexico, maintaining the highest proportion of vacancies, despite a slight decline from 10.6% in 2021 to 10.4% in 2024.
Meanwhile, the manufacturing sector has shown a significant rebound, rising from 8.2% of vacancies in 2023 to 10.1% in 2024, consolidating itself as the second sector with the most job offers.
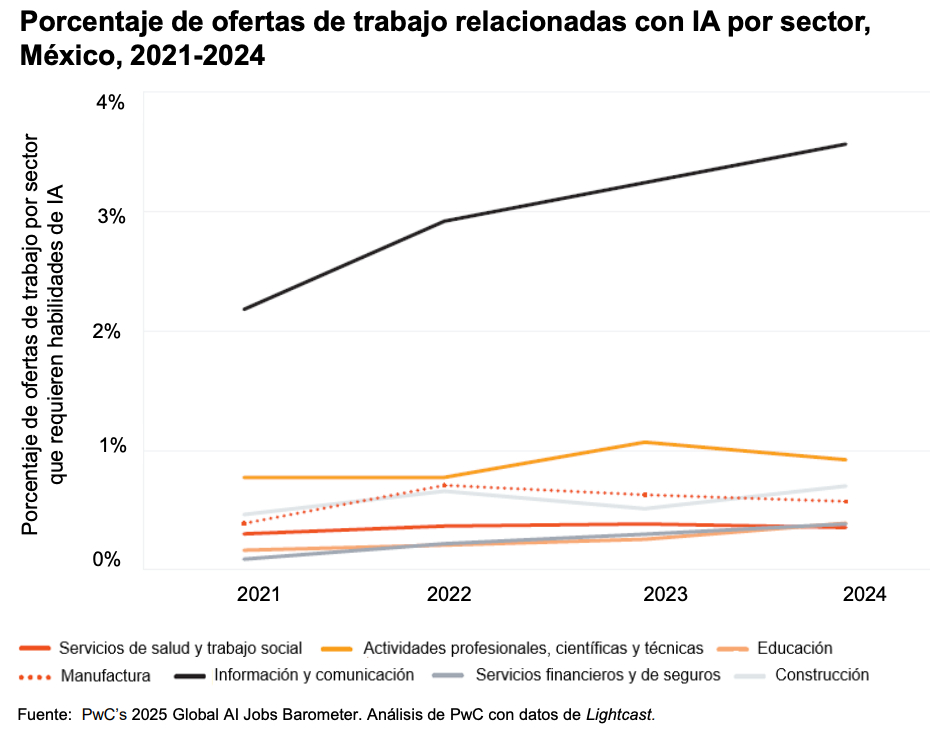
In terms of specific AI-related skills, the information and communications sector leads the demand, with steady growth from 2.2% in 2021 to over 3.6% in 2024. Other sectors, such as finance, insurance, manufacturing, and healthcare services, still show a slower adoption of AI, with less than 1% of their vacancies focused on this area.
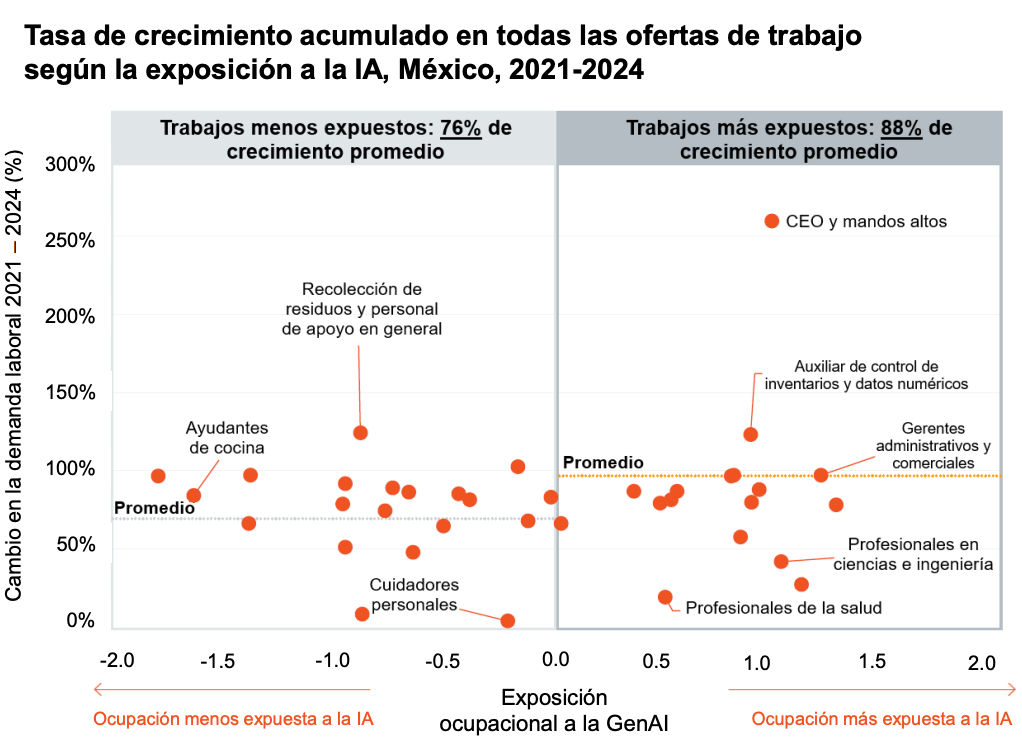
What impact does artificial intelligence have on different types of occupations?
The PwC Barometer reveals that jobs exposed to artificial intelligence have experienced significant growth. Between 2021 and 2024, vacancies in occupations highly exposed to AI increased by 88%.
Particularly striking is the case of CEO and senior management positions, where vacancies grew by 250%, reflecting that AI adoption not only transforms technical positions but also leadership levels.
In the specific case of generative AI, growth in exposed occupations reached 84%, with senior positions once again topping the list, with an astonishing 600% increase in job offers.
Artificial intelligence and educational requirements in the Mexican labor market
One of the most interesting findings from PwC’s report is the decline in degree requirements for AI-related jobs.
Between 2021 and 2024, jobs with high AI exposure saw university degree requirements drop from 14% to 12%, while for less exposed jobs, the decline was from 2% to 1%. Although a gap still exists, the data suggests that AI is helping to democratize access to skilled jobs by reducing formal entry barriers.
In the case of jobs related to augmented AI, degree requirements fell by 15%, dropping from 18% to 15%, while in automated jobs the decline was from 11% to 10%.
This phenomenon suggests that practical experience and technical skills in artificial intelligence may carry more weight than traditional academic degrees in the hiring process.
What are the implications of this outlook for business leaders in Mexico?
PwC identifies five key recommendations for business leaders facing the growing influence of artificial intelligence:
- Accelerate AI adoption by leveraging global best practices and overcoming initial barriers.
- Use AI to transform business models, generating new revenue streams and increasing productivity.
- Drive organizational growth and agility, avoiding limiting AI use solely to workforce reductions.
- Develop specialized talent through training and reskilling strategies to close skills gaps.
- Build trust in AI through responsible implementation, with clear governance and a focus on people’s well-being.